Last year, a group of three camera department women got together to plan a simple yard sale — that ballooned into the event of the year. Those women were Erin Zellers, Tina Somphone and myself. And we had to go bigger and better this year.
I wrote about the first one here: https://bridgetlamonica.com/2024/09/11/the-atlanta-film-yard-sale-and-building-a-film-community/

Being a filmmaker doesn’t mean you are an artist on an island, creating alone. Film production is the ultimate group project. (sorry kids in high school, you still have to get along with other people!) Just as you would make a film with a group of dedicated people, the yard sale event comes together thanks to a wide network of people, from the three organizers, to the volunteers, to the sponsors, to the vendors and the attendees.
There was a lot of well-intentioned pressure from Year 1 to keep going. We didn’t even finish having the event last year before people were asking us when we would do it again. “Twice a year?” some people suggested. We all turned pale. “Once a year is fine” we assured them.
As 2025 dawned, we got to work.
Looking at what we got right and what needed work last year, we started figuring things out. One biggie was that we needed more space. We absolutely packed 24ATL last year, the LED Volume Studio in Doraville GA. It was a great space (and that wall is super cool, you should really check it out) but we ended up shortchanging people on space and didnt’ want to do that again.
Plus the need was simply greater this year. I know I haven’t discussed it on the blog much but I have talked endlessly about this to folks in person. The film industry is not in a great place right now. People are making the decision to either transition out of the industry entirely, or are holding on with their fingertips and hoping things will pick up work-wise. For this reason, there’s a number of people who just need to make some money or want to transition their business to something else. We had plenty of people who wanted to sell at the event.
Our sponsors this year made it possible to get any further. You can’t host an event without money to organize it.
Tier 2 Sponsors
You can see Local 600’s writeup about the event here.
Tier 1
Yes, we had a lot of sponsors! They donated money, prizes for the drawing, and more. We also had a surprise bonus drawing prize from Panavision! Super awesome.
PC&E (Production Consultants & Equipment) became our venue for the event. Not only do they rent out a lot of film gear in the local film industry here, they also have an enormous sound stage that we would end up filling. And then some.


We filled every available space, from the entirety of Stage 1’s 9400 sq ft to the staging area leading to it and the outside. We had people everywhere! Plus food trucks. Plus activities like a scavenger hunt.
This year we were able to raise money for a cause that’s near and dear to a lot of members of the film industry, the Sarah Jones Film Foundation. The foundation honors the memory of 27 year old camera assistant Sarah Jones, who tragically lost her life in February 2014 due to an accident on the set of Midnight Rider. The foundation provides education and awareness, film safety grants, and even a wonderful film internship program. You can learn more about the foundation here.

Thanks to our donated items, our drawing prizes, our vendors and sponsors, we were able to raise $2500 for the foundation.
We also held demonstrations this year! As is typicaly with the film production life, we had a couple cancellations that had to be filled, and everyone who did a demonstration did an amazing job.
The demonstrations included an excellent “how to film stunts” demo with Good Slate Pictures. They also have a YouTube channel so you should definitely check out their stuff! Their YouTube is called Behind the Stunts.

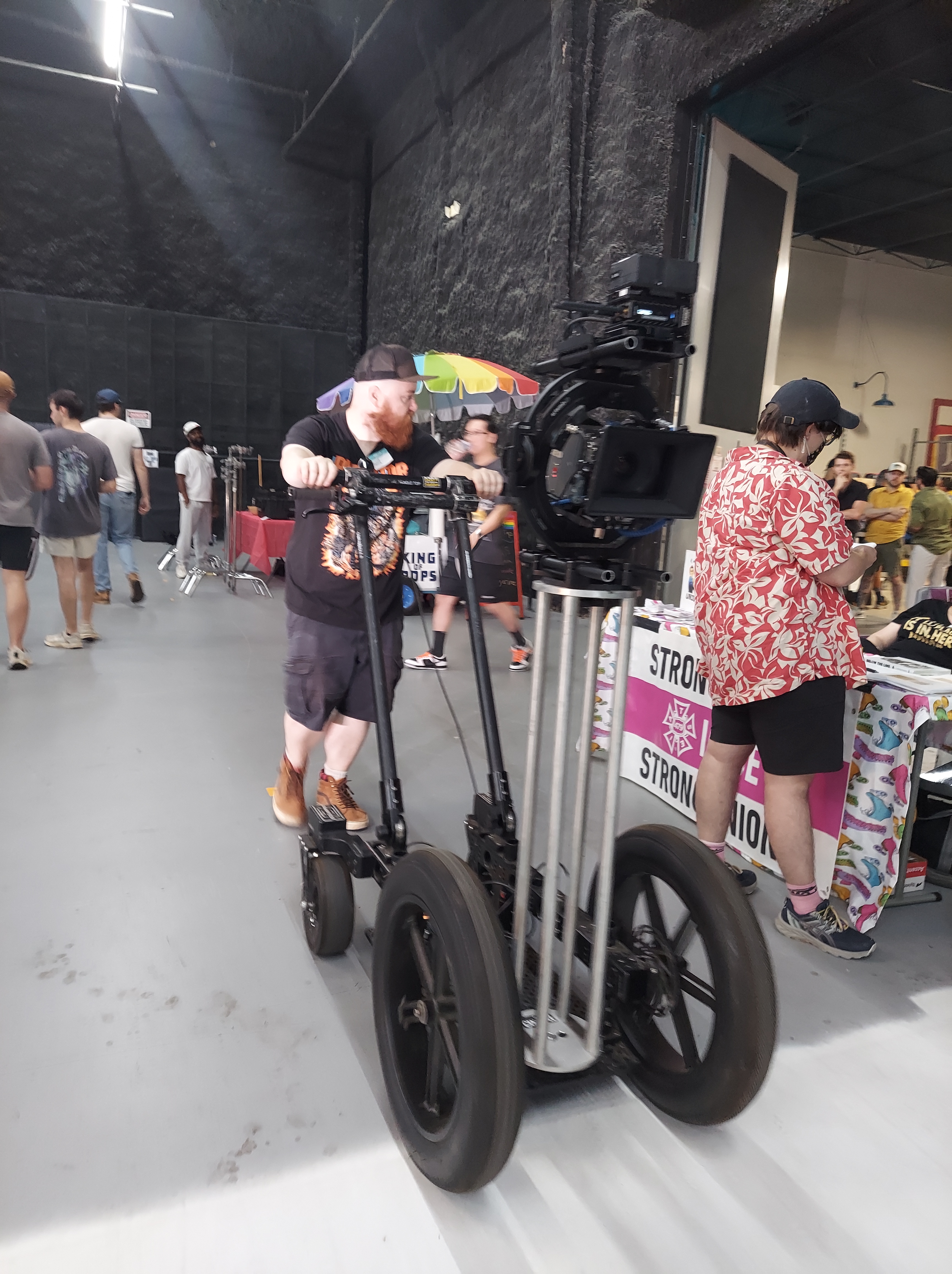
Chris Roe, ARRI Certified TRINITY Operator, Cinematographer and Steadicam Operator, brought his cool rickshaw with remote head! Folks got to try to remote head for themselves as the rickshaw roamed the space.
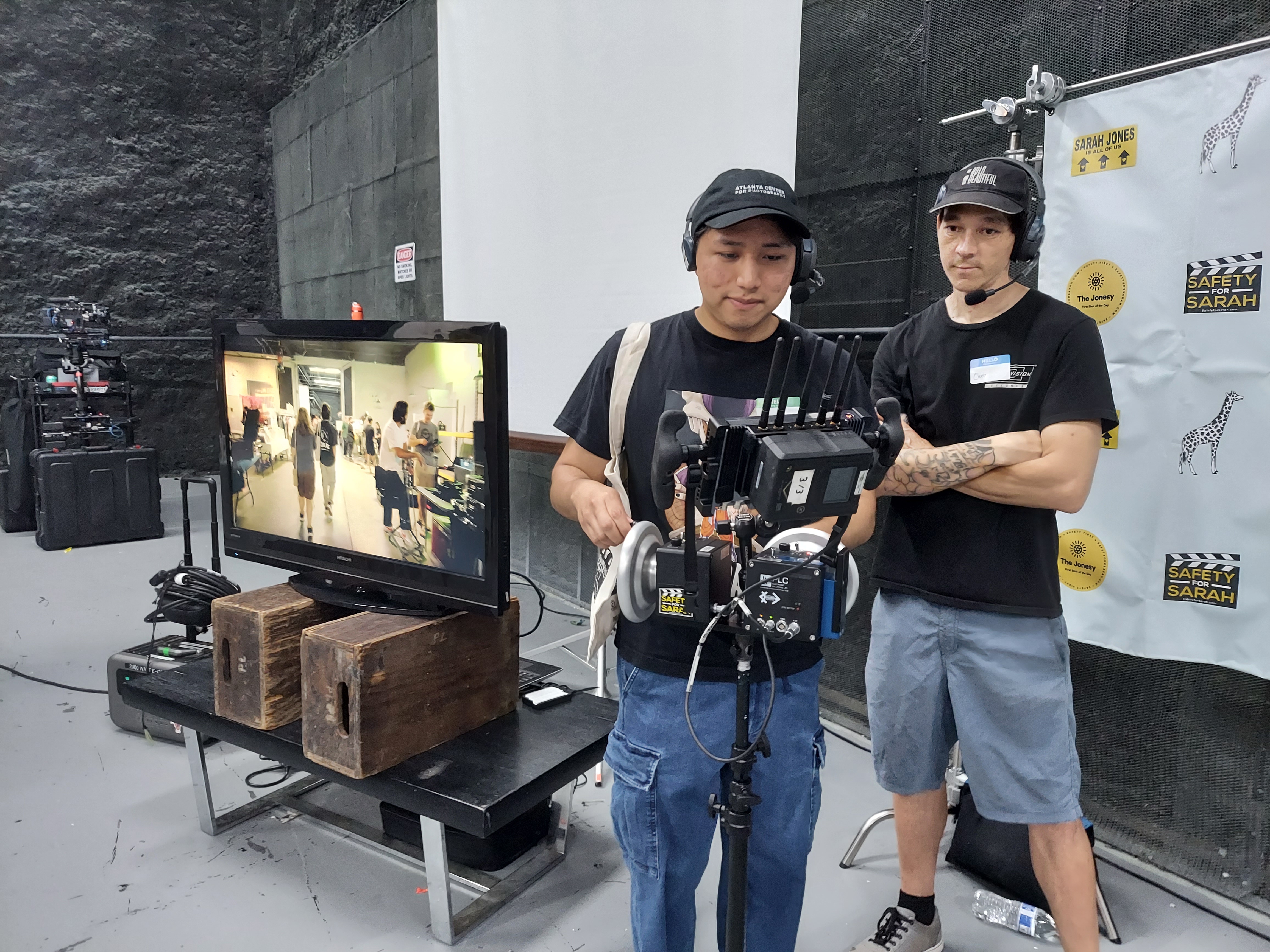


Kenya Campbell and Deanna Griffin did a DP/Gaffer fireside chat. It was great information to share with our audience as experience levels varied. Plus it is always great to learn new tips, tricks, and practical information to make you better at your job!
I can’t say enough about how this community came together! This, my friends, is what the film industry is all about. Working together towards a common goal. Sharing education and resources. Having a good time with your friends.
We’ll see you at the next one.
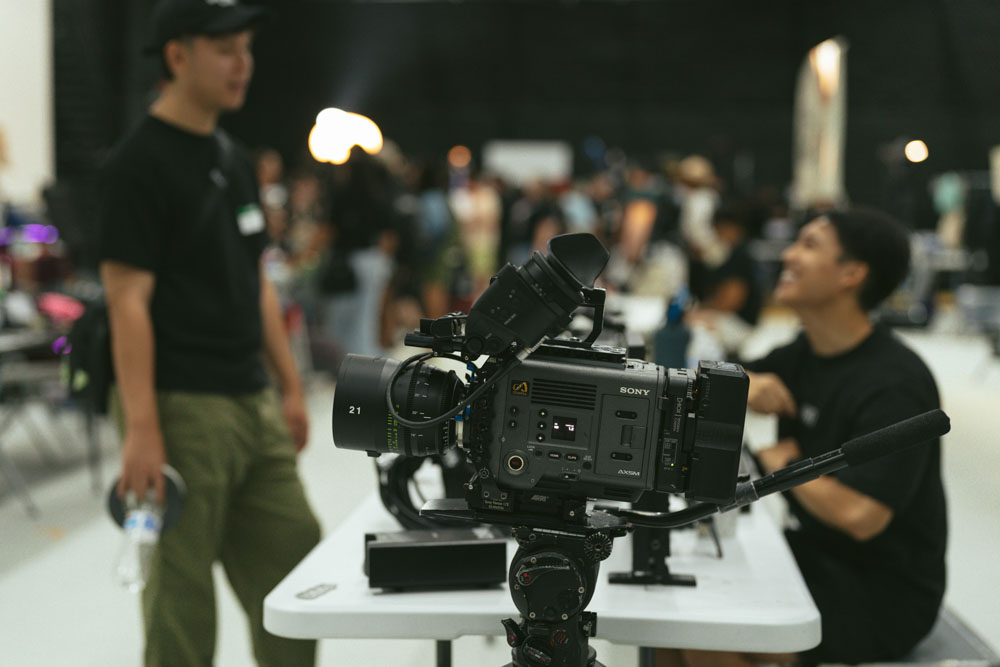
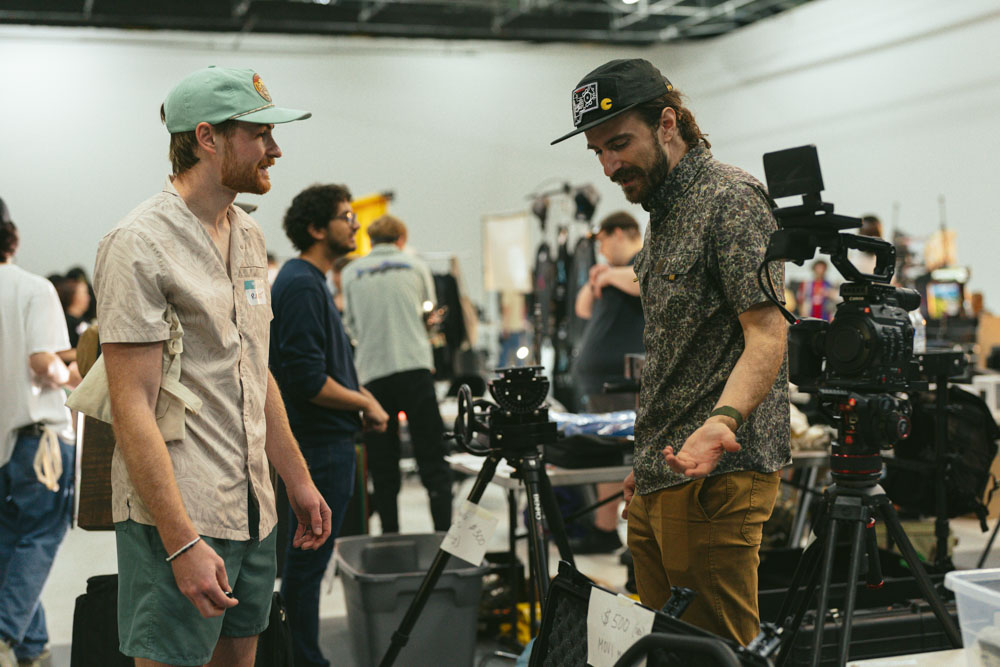
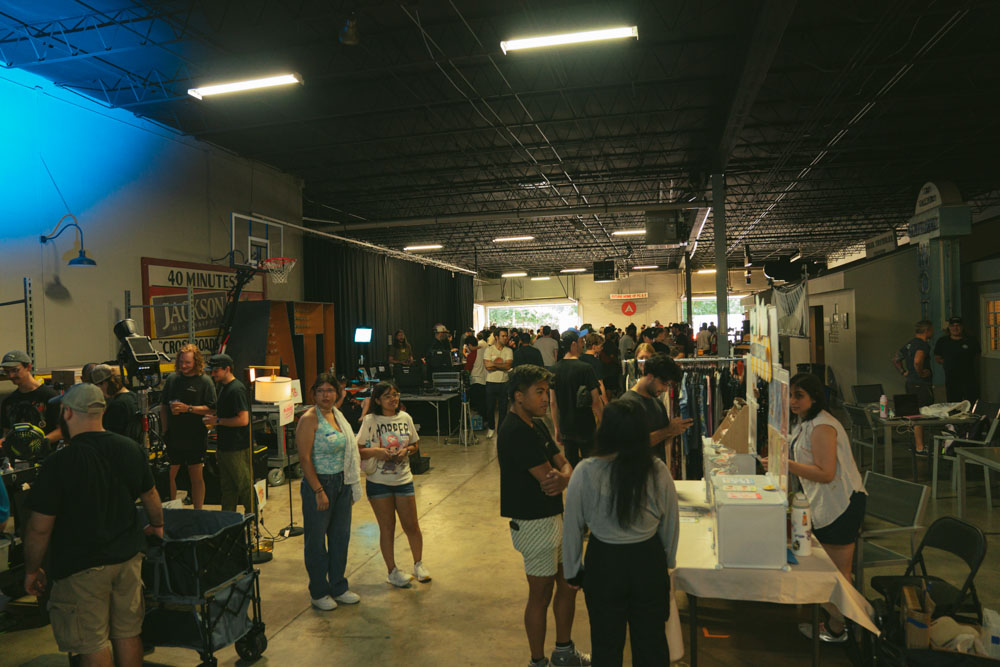







Photo Credit: Local 600 Still Photographer Josh Stringer