I was one of the lucky 1.1 million people who saw the Stranger Things finale at the movie theater New Years Eve. Screenings were sold out around the country to celebrate the culmination of 9 years of a popular Netflix show. This also got me thinking about the theater experience and what is needed to get butts in seats in a time when people morbidly declare the movie theater is dead.
I went with a group of friends to the historic Tara Theatre. The Tara is an Atlanta landmark, an arthouse theater featuring 4 screens, independent showings, and old school charm. The Tara was one of approximately 600 theaters that did this special Netflix screening over New Years. It was also the location of a scene between Lucas and Max near the end of the finale. The Tara even gifted free movie passes to the lucky two who sat in those seats. Thanks to my friend Charles who came up with the idea.
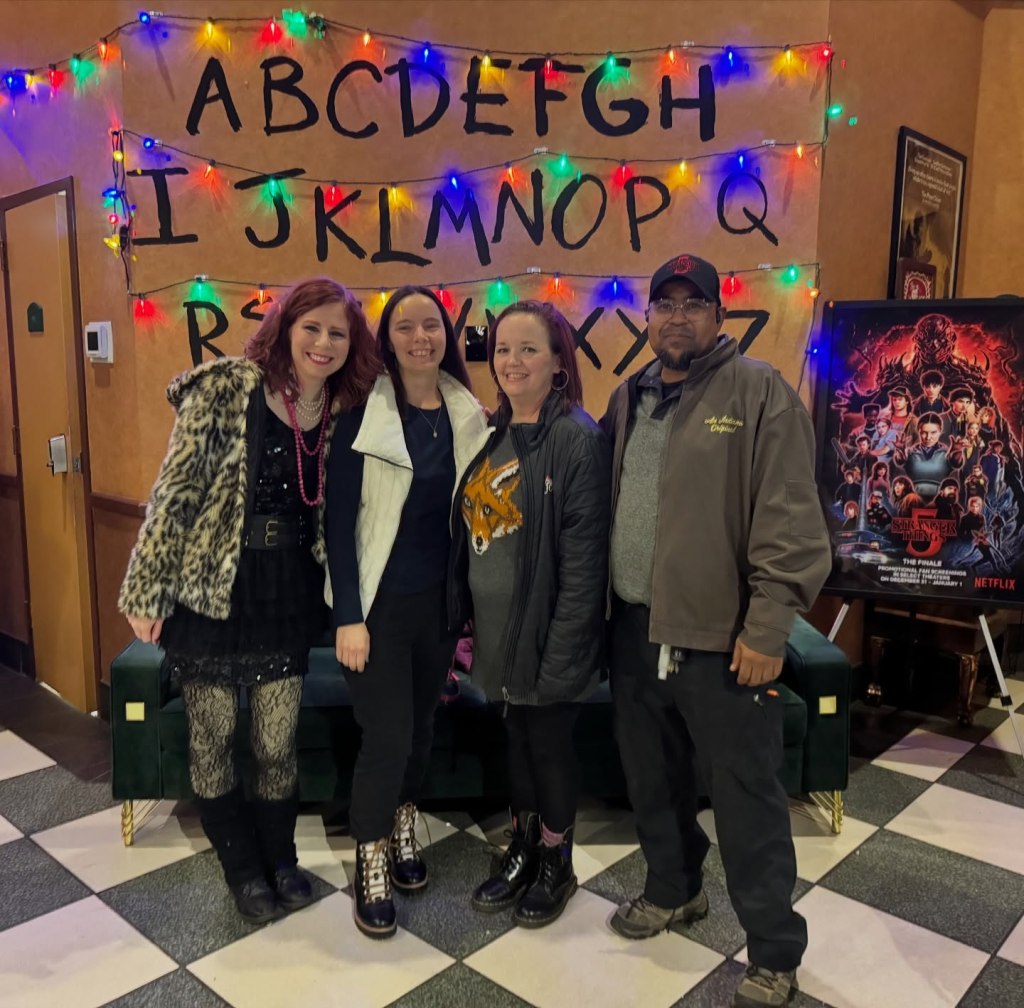

The showing I went to at the Tara Theatre was a whopping $7 for a ticket. Seven dollars!? In THIS economy? Considering many movie ticket prices in Atlanta average around $15-20 for a basic showing, that was a steal. Tickets sold out in advance of the screening date, and from what I heard, that was the case around the country. Folks wanted to see this in theaters with their fellow fans.
The two-day screening over New Years netted theaters $25-30 million in sales – though not necessarily in ticket sales. According to Deadline, the actor’s residuals for the Netflix show kept them from selling actual tickets, so they sold ticket vouchers. It’s a loophole.
Netflix and movie theaters did a similar collab in August 2025 when they rereleased K POP Demon Hunters to the tune of $19m, and got Netflix its first No 1 at the box office.
Streaming culture has changed the way we do TV. Many stories are tailored to the bingeable short seasons of streaming television. But the lines are becoming blurred as streamers like Netflix, Apple TV and HBO put out their streaming content in movie theaters. Partly to gain an audience, and also partly to take part in those award ceremonies.
But this culture has also contributed to less folks going to the movie theater. You can argue with me about this, but why should folks go see something in the theater if it’s going to be on their TV in a month or two?
Fall Guy, a movie I really enjoyed, barely got to get its legs up under itself before it was pulled from theaters and thrust onto the streamers. It was actually getting good reviews and word of mouth, but wasn’t given the chance it needed. Fall Guy was released May 3, 2024, made $180 million against its $125-150 million budget, and was pulled from theaters for “underperforming” its opening week. It was on the streaming service just 17 days after its release. When the film was uploaded to Peacock, it set a streaming record, becoming that platform’s biggest film debut.
Folks have been trying to predict the end of the movie theater experience for years.
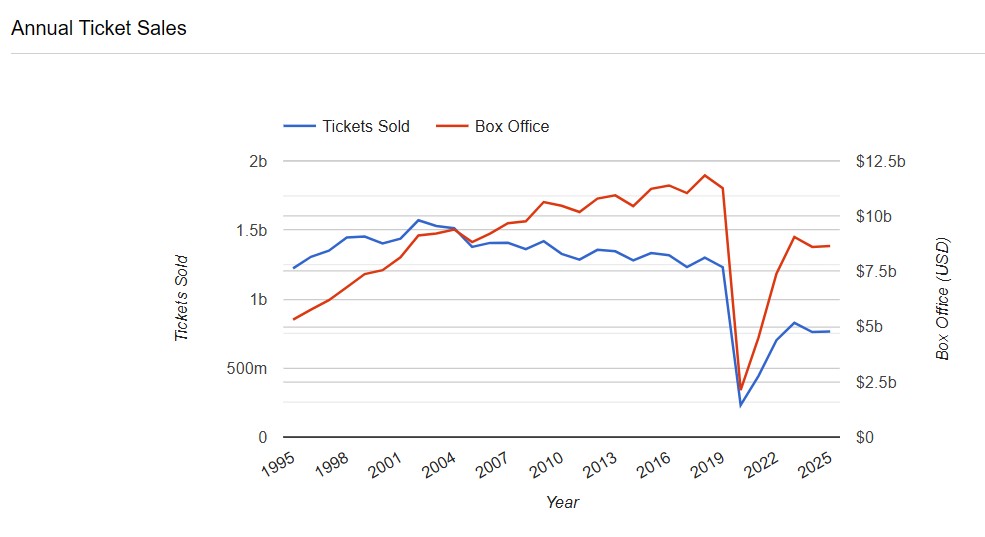
This graph from The Numbers (great resource for these stats) shows that sharp decline into 2020 (we all know what happened there) and then a slow climb back up to where things stand now, which is quite a bit below where the numbers were headed in 2019. And this can be scary to those who make movies and to those who cherish them.
Audiences do enjoy the experience of being in a movie theater. For the most part. I mean you could listen to some of my friends who critique how oppressively loud the sound is or how rude their fellow patrons are. But for the right screening, people will put butts in seats.
Where’s the incentive to do so when tickets are pricey and you only have to wait a month or two (or 17 days) and it’ll be out on any one of the streaming services you have?
Speaking of price, here’s the cost for two adults and 1 child to see the new Zootopia film:
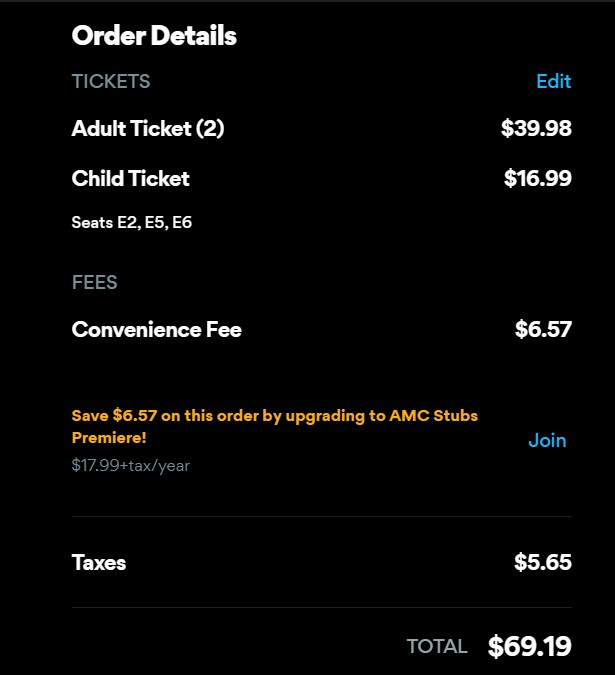
This is the cost for AMC Madison Yards for 6pm on 1/3/2026
Almost $70?! And a convenience fee for using the website. That’s just silly.
For a deal, you can sign up for AMC Stubs or Movie Pass or Regal Crown Club or just go on discounted Tuesdays… but the point still stands. Going to the movies can be expensive, especially for families.
In 2022 National Cinema Day was celebrated with a $3 movie ticket day, which was honored by numerous theater chains. People flocked to the movie theaters, seeing multiple movies in a day and finally watching movies they’d missed earlier in the year. It was a great promotion, and I’m sad that when I search for it now, I haven’t seen it done in years.
There’s a way to keep the movie theater business alive. I think we’re still searching for the correct recipe for success, but special exclusive screenings certainly don’t hurt.
Sources:
The Tara Theatre: https://www.taraatlanta.com/about–contact
The Numbers – Domestic Movie Theatrical Market Summary 1995 to 2025
https://www.the-numbers.com/market/
‘The Fall Guy’ is now streaming after just 17 days in theaters. Are summer movies in trouble?