The WGA and SAG-AFTRA are both on strike against the Alliance of Motion Picture and Television Producers (AMPTP) halting TV and film productions and leading to a very sparse year financially for many film workers. They’re just asking for more money, right? Yes and no. This is certainly not a case of greed from the average film worker, but from corporate CEOs who make hundreds of millions of dollars a year while balking at a small percentage that writers are asking for. To put it in perspective, since 2018 writers have seen an inflation-adjusted fall in revenue of 14%. For writer-producers it’s worse at 23%. In recent years, the numbers of writers working at a WGA minimum went from a third to half of all writers. Meanwhile SAG-AFTRA actors report paltry residuals and popular TV shows that didn’t properly compensate them either, and a big culprit is streaming.
The WGA Strike Began May 2, 2023
The WGA went on strike in May when negotiations broke down. How far apart was the WGA’s proposal from the AMPTP counter offer? The WGA asked for a pay increase for members totaling $429 million per year (that’s only about 5% on WGA minimums). The AMPTP countered at $86 million per year, an amount they called “generous.”
You can consult this page to see the WGA’s terms and the AMPTP counter offers.
The WGA has gone on strike for several reasons, one of them being paltry residuals for streaming shows. Residuals are compensation for a performer when their work is re-run, syndicated to another network, or sold as a physical media such as a DVD box set to name a few. Streaming obviously complicates this because programs are not broadcast in the same fashion as on traditional TV.
“Over the past decade, while our employers have increased their profits by tens of billions, they have embraced business practices that have slashed our compensation and residuals and undermined our working conditions,” said the WGA Negotiation committee to its members prior to the strike beginning.
Surprisingly, WGA West’s fiscal report in March 31, 2022 reported an “all time high” in guild collected residuals. How does that make sense when writers claim they’re making less?
Because they are making less!
The total residuals may appear higher, but that is due to the volume of extra projects being made. It’s no longer just theatrical releases and network TV. There is a cornucopia of different streaming platforms all vying for a catalogue of material to get you to sign up for another subscription service.
Charles Slocum, assistant executive director at the WGA West, indicated that residuals slashing was taking place on a per-program basis, and the major culprit was streaming services.
And so, when WGA contracts were coming to an end this year, residuals were one of the main points they would negotiate for — as well as not having writers replaced by the likes of ChatGPT.

Slocum also made the point that companies have not agreed to pay residuals at broadcast levels for streaming programs. “If you write for a streamer, you get two residuals payments – one for domestic streaming and one for foreign streaming. It’s a set amount of money. If it’s a big hit, you do not get paid more residuals in streaming, whereas in the broadcast model, you do because of its success. That’s the sense that residuals were slashed – they have not agreed to a success factor when a program is made for streaming.”

Many writers, actors, and other film industry professionals have taken to social media to explain what position they are in. Screenwriter Daniel Kwan, Oscar-winner for Everything Everywhere All at Once, said on Twitter, “It’s about maintaining a healthy middle/working class of writers in our industry. It’s about showing our collective strength as new tech threatens to take away our leverage.”
The average person may assume that screenwriters (and actors!) are making so much money already that this argument is unnecessary. But the truth is, the majority fall into middle class status or lower. Only a small percentage make the insane bucks that make headlines.

Shrinking writer’s rooms has also been a factor that has plagued modern writers. In traditional TV, you’d have a group of people hammering out episode ideas, sharing script writing duties for 20+ episode seasons. Now, with streaming’s angle towards shorter seasons (8 episodes seems the norm these days) and fewer writers, the entire process has shifted. Shorter seasons and smaller rooms equals fewers weeks of pay and more gaps in work for writers and actors alike
SAG-AFTRA Strike Began July 14, 2023
Actors too, are striking for better conditions. They decry similar concerns such as waning residuals from streaming to A.I. creating virtual versions of actors and replacing them, the actors were ready to put their foot down and join the WGA on the picket line.
“There has been a sea change in the entertainment industry, from the proliferation of streaming platforms to the recent explosion of generative AI, and at stake is the ability of our members to make a living,” said SAG-AFTRA Chief Negotiator Duncan Crabtree-Ireland. “We must ensure that new developments in the entertainment industry are not used to devalue or disrespect the performers who bring productions to life.”
The culture’s shift to streaming has led to shorter season runs, and therefore fewer episodes and less work for recurring performers on shows.
Most actors, like the writers, do not make the big bucks that make readers of Variety blush. Many are considered middle class or even struggling to get by. As the strike was authorized, numerous actors took to Twitter to provide anecdotes on why the strike was necessary.

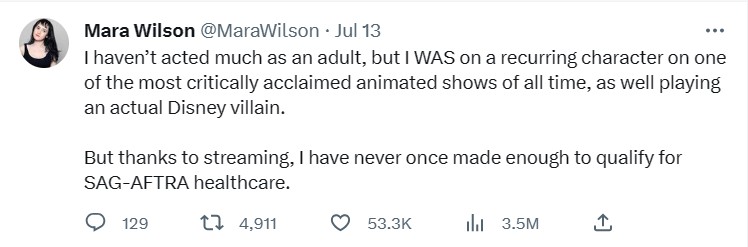
The popularization of A.I. tech has made both writers and actors nervous about the reality of losing their jobs. This is a huge topic, and difficult for me to cover without this post ballooning into a novel’s length, but suffice to say that AMPTP has unironically looked at A.I. as a cost-cutting maneuver to replace people.
This post went around recently by Justine Bateman, A.I. consultant to SAG-AFTRA during the negotiations.:

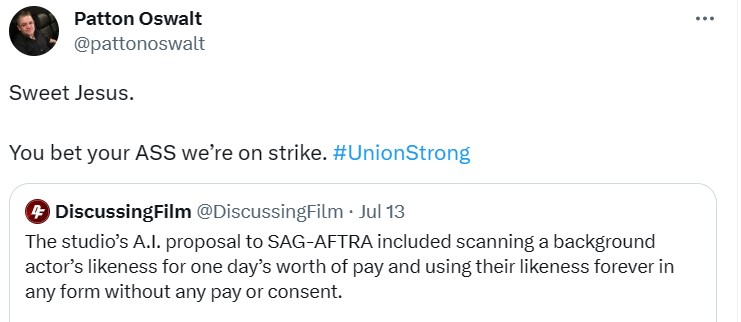
All indicators are showing that we’re going to be in this for the long haul.
Sources:
Deadline: Are Streaming Residuals Being Slashed? As WGA’s Own Data Shows, It’s Complicated
Tensions from the last writers’ strike cast a shadow over current labor fight
Why Actors Are Going on Strike
Mini Rooms Drive Major Controversy as Creative Community Feels Strain of TV’s Vast Expansion
SAG actors strike, joining Hollywood writers. What are we supposed to do now? Read?
































